AADS-T
What is AADS-T?
The AADS-T tool enables the modeling of a subset of AADL including the Behavioral Annex for purposes of implementation and simulation. The starting point of the simulator will be an AADL specification. This AADL specification must contain a minimum functionality described by means of some AADL properties in order to enable a proper simulation of the model. The AADL model will be parsed by AADS-T and a model defined with POSIX / C++ and XML will be obtained. This model will be simulated in order to check whether the AADL constraints are fulfilled. As the design process advances and the real functionalities are attached to the software components using the corresponding source code, the value of these properties will be refined. These refined properties will be added to the AADL model and a new model will be generated by AADS-T to check if the constraints are still fulfilled.
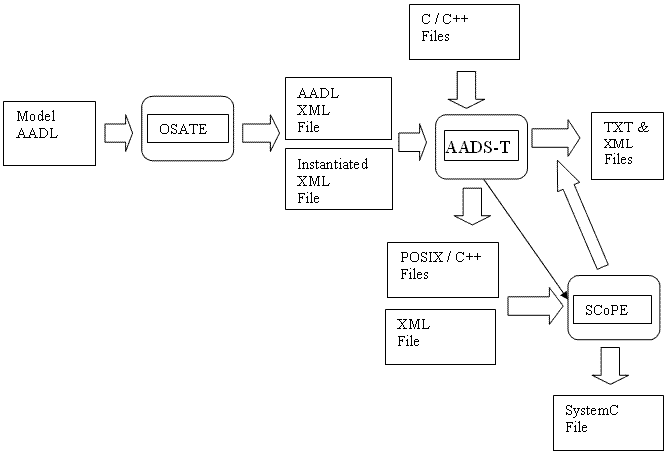
When the AADS-T tool is initiated it requests the name of two AADL XML files. One of these files is just the AADL model written in XML. The other is the result of an instantiation of a system implementation of a textual or object AADL model obtained with OSATE, a plug-in of the Eclipse platform used to process AADL models (see the figure). These files are written in XML as they are easier to analyze using AADS-T because of the use of SAX.
Files containing the actual source code of the subprograms of the AADL model can be supplied to AADS-T, although it is not mandatory. If they are supplied, the simulation and performance analysis done with SCoPE will be more realistic, as this source code is embedded in the POSIX / C++ files generated by AADS-T.
Once the XML files have been parsed by AADS-T, files written in C++ with the extensions .h and .cpp and one XML file are created. The number and names of the files created depend on the AADL model parsed. The C++ files use POSIX functions and the XML file must be as specified to be used by the SCoPE tool. The source code in C++ produced by AADS-T is compatible with the Ravenscar Computational Model.
AADS-T offers the possibility to the user of launching the SCoPE tool automatically. If the user launches SCoPE from AADS-T, AADS-T generates one .txt file and one .xml file from the output of SCoPE, containing the most important data about the simulation and performance analyses such as use of CPU, core energy consumed, number of instructions executed and others.
Moreover, a file is generated with the SystemC description of the AADL model.
Relationship among OSATE, AADS-T and SCoPE.
|